1. 피어슨 상관계수
두 연속형 변수 간의 선형 관계를 측정하는 지표로 -1에서 1 사이의 값을 가진다. 1은 완전한 양의 선형, -1은 완전한 음의 선형, 0은 선형 관계가 없음을 의미한다.
공부 시간과 시험 점수 간의 선형적인 관계가 예상될 때 사용하며 비선형 관계에서는 사용할 수 없다.
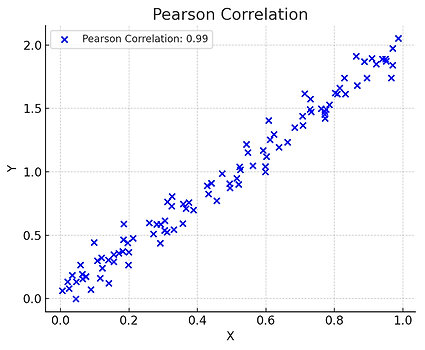
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from scipy.stats import pearsonr
# 예시 데이터 생성
np.random.seed(0)
study_hours = np.random.rand(100) * 10
exam_scores = 3 * study_hours + np.random.randn(100) * 5
# 데이터프레임 생성
df = pd.DataFrame({'Study Hours': study_hours, 'Exam Scores': exam_scores})
# 피어슨 상관계수 계산
pearson_corr, _ = pearsonr(df['Study Hours'], df['Exam Scores'])
print(f"피어슨 상관계수: {pearson_corr}")
# 상관관계 히트맵 시각화
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
plt.title('pearson coefficient heatmap')
plt.show()
2. 비모수 상관계수
데이터가 정규분포를 따르지 않거나 변수들이 순서형 데이터일 때 또는, 데이터의 분포에 대한 가정 없이 두 변수 간의 상관관계를 측정할 때 사용한다.
- 스피어만 상관계수
X와 Y의 순위 관계를 보여줘 두 변수의 순위 간의 일관성을 측정한다. 값은 -1에서 1 사이로 해석되며 켄달 타우 상관계수 보다 데이터 내 편차와 에러에 민감하다.
- 켄달의 타우 비선형 상관계수
X와 Y의 비선형 관계를 보여준다. 순위 간의 일치 쌍 및 불일치 쌍의 비율을 바탕으로 계산한다. 비선형 관계를 탐지하는 데 유용하다.
from scipy.stats import spearmanr, kendalltau
# 예시 데이터 생성
np.random.seed(0)
customer_satisfaction = np.random.rand(100)
repurchase_intent = 3 * customer_satisfaction + np.random.randn(100) * 0.5
# 데이터프레임 생성
df = pd.DataFrame({'Customer Satisfaction': customer_satisfaction, 'Repurchase Intent': repurchase_intent})
# 스피어만 상관계수 계산
spearman_corr, _ = spearmanr(df['Customer Satisfaction'], df['Repurchase Intent'])
print(f"스피어만 상관계수: {spearman_corr}")
# 켄달의 타우 상관계수 계산
kendall_corr, _ = kendalltau(df['Customer Satisfaction'], df['Repurchase Intent'])
print(f"켄달의 타우 상관계수: {kendall_corr}")
# 상관관계 히트맵 시각화
sns.heatmap(df.corr(method='spearman'), annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
plt.title('spearman coefficient heatmap')
plt.show()
3. 상호정보 상관계수
변수 간의 정보 의존성을 바탕으로 비선형 관계를 탐지한다. 서로의 정보에 대한 불확실성을 줄이는 정도를 바탕으로 계산하며 범주형 데이터에 대해서도 적용 가능하다.
두 변수가 범주형 변수일 때 또는 비선형적이고 복잡한 관계를 탐지하고자 할 때 사용한다.
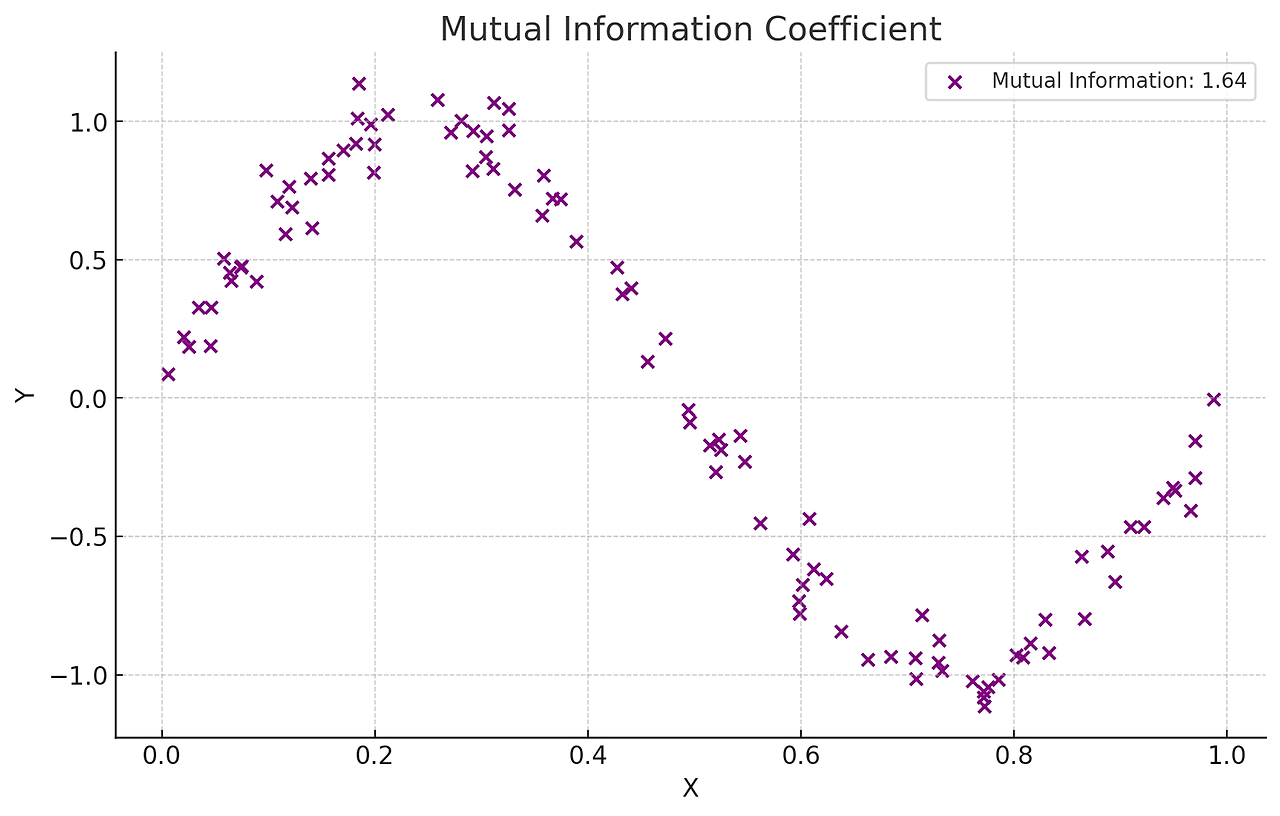
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import mutual_info_score
# 범주형 예제 데이터
X = np.array(['cat', 'dog', 'cat', 'cat', 'dog', 'dog', 'cat', 'dog', 'dog', 'cat'])
Y = np.array(['high', 'low', 'high', 'high', 'low', 'low', 'high', 'low', 'low', 'high'])
# 상호 정보량 계산
mi = mutual_info_score(X, Y)
print(f"Mutual Information (categorical): {mi}")'내배캠 - TIL > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [TIL] Python 베이직 - 6회차 (0) | 2024.08.06 |
|---|---|
| [TIL] 통계학 기초 - 6주차 (0) | 2024.08.05 |
| [TIL] 통계학 기초 - 4주차 (0) | 2024.08.02 |
| [TIL] Python 챌린지 - 3, 4회차 (0) | 2024.08.02 |
| [TIL] 통계학 기초 - 3주차 (0) | 2024.08.02 |